Did you know a single strength-training movement can activate over 75% of your body’s muscle mass in one motion? Fitness researchers confirm this full-body engagement isn’t just possible – it’s exactly what happens during a properly executed barbell lift.
This powerhouse exercise isn’t just for gym enthusiasts. From parents lifting toddlers to workers moving boxes, its movement pattern mirrors daily life. The secret lies in how it coordinates your posterior chain – the critical network of tissues running from heels to shoulders.
You’ll discover how this fundamental lift:
- Strengthens your foundation (think hips and thighs)
- Stabilizes your core during heavy loads
- Enhances grip strength through sustained tension
Proper form transforms this move into a real-world superpower. Whether you’re hauling luggage or gardening, the strength developed translates directly to daily tasks. We’ll break down the science behind muscle activation and share expert tips to maximize results safely.
Key Takeaways
- Engages multiple muscle groups from feet to shoulders simultaneously
- Builds practical strength for everyday lifting scenarios
- Requires proper form to prevent injury and maximize benefits
- Offers variations suitable for all experience levels
- Enhances posture through spinal stabilization practice
- Develops grip endurance as a valuable secondary benefit
Introduction to Deadlifts and Their Benefits
Imagine an exercise that trains your entire posterior chain while mimicking natural human movements. That’s exactly what makes this powerhouse movement stand out. “You’re not just lifting weight – you’re rehearsing biomechanics our bodies evolved to perform,” explains Dr. Elena Torres, sports physical therapist.

Three key advantages set this compound exercise apart:
| Feature | Traditional Exercises | Compound Lift |
|---|---|---|
| Muscles Engaged | 3-5 groups | 10+ groups |
| Time Efficiency | 30 mins/session | 15 mins/session |
| Functional Carryover | Limited | High |
The magic happens through coordinated effort. Your glutes and hamstrings generate power while core stabilizers protect your spine. This synergy creates strength that helps you:
- Carry groceries without strain
- Maintain better posture at desks
- Prevent back injuries during chores
“For every minute spent mastering this movement, you gain hours of injury-free living.”
What truly sets it apart? The real-world translation. Unlike isolated machine exercises, this full-body challenge builds coordination that enhances sports performance and daily activities. Plus, you’re strengthening the often-overlooked backside muscles crucial for balance and alignment.
Understanding Deadlifts as a Compound Exercise
What if one gym move could replace half your workout routine? That’s the power of multi-joint training. Unlike isolated curls or leg extensions, these lifts mirror how your body naturally operates – with multiple areas collaborating seamlessly.
Movement Patterns You Already Use
Ever loaded groceries into your trunk or scooped up a toddler? You’ve performed a hip hinge without realizing it. This fundamental motion – bending at the hips while keeping your spine neutral – forms the foundation of countless daily tasks. Physical therapists call it “the body’s loading mechanism” for good reason.
Common real-world applications include:
- Lugging laundry baskets upstairs
- Shoveling snow without back strain
- Rearranging living room furniture
Smart Training for Busy Schedules
Time-crunched individuals gain major advantages from compound movements. A 2023 study showed 20-minute sessions focusing on multi-joint exercises build strength 34% faster than single-muscle workouts. Here’s why:
| Workout Type | Muscles Trained | Calorie Burn |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation | 1-2 groups | 80-100 |
| Compound | 6+ groups | 150-200 |
Fitness coach Marco Ruiz puts it simply:
“You’re not just exercising – you’re upgrading how your body handles real-world challenges.”
Mastering these patterns does more than build strength. It creates movement literacy – your body remembers proper form during unexpected demands, like catching a slipping package or helping a friend move.
Key Muscle Groups Targeted by Deadlifts
Think of your body as a kinetic chain during heavy lifts. The most effective movements engage multiple areas simultaneously, creating strength that transfers to daily activities. Let’s explore how specific tissues collaborate during this full-body effort.
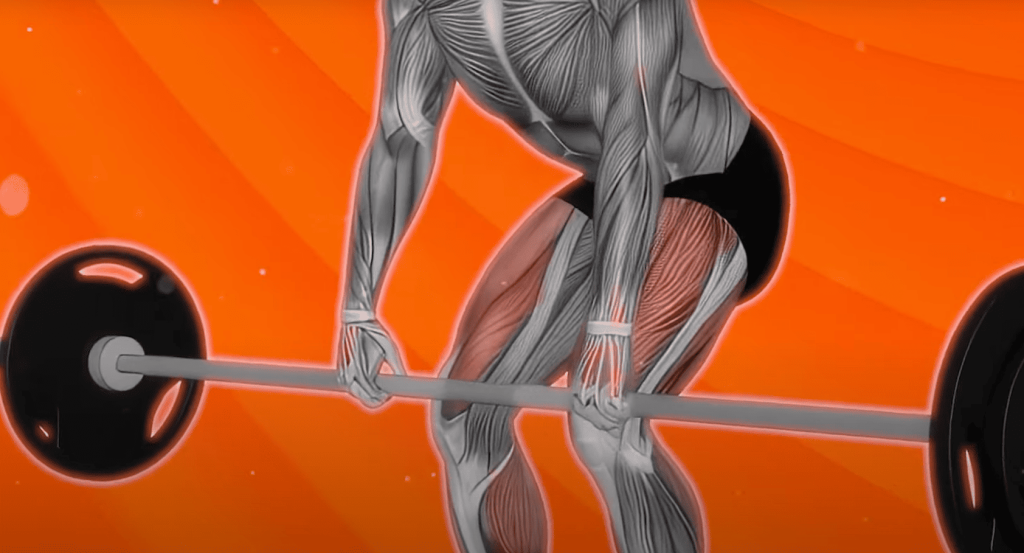
Powerhouse Players: Hips and Back
Your glutes act as the engine during hip extension, generating upward force to lift weights. Paired with hamstrings, they form a dynamic duo that powers the hinge motion. Meanwhile, spinal erectors work overtime to maintain posture – imagine steel cables keeping your back straight against resistance.
| Muscle Group | Primary Role | Real-World Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Glutes | Hip extension | Climbing stairs effortlessly |
| Hamstrings | Knee stabilization | Bending safely to lift packages |
| Spinal Erectors | Spinal alignment | Preventing back pain at work |
Stabilizing Crew: Midsection and Upper Body
Core muscles form a natural weightlifting belt, bracing your torso from all sides. Lats pull double duty – they keep the bar close to your body while stabilizing shoulders. Don’t overlook grip strength either; forearms maintain control like vice grips on heavy objects.
“Proper lifting teaches your body to work as a team – no muscle left behind.”
Secondary contributors like trapezius muscles prevent shoulder rounding, while calves and quads provide foundational support. This coordinated effort explains why multi-joint exercises remain unparalleled for functional fitness.
In-Depth Look at Deadlift Muscles Worked
Every successful barbell pull becomes a symphony of tissue collaboration. From your heels to your shoulders, different groups activate in precise sequence to move weight efficiently. Let’s examine how your body coordinates this complex movement pattern.
Muscle Activation Timeline
The setup phase engages your core first. Transverse abdominis and spinal erectors tighten like a corset before the bar leaves the floor. As you initiate the pull:
- Hamstrings lengthen while glutes generate upward thrust
- Lats pull shoulders back to maintain bar proximity
- Trapezius stabilizes scapulae during ascent
At lockout, hip flexors complete extension as calves anchor your stance. This sequential firing pattern mirrors how you’d lift heavy boxes – legs powering the motion while back muscles prevent rounding.
Myths vs Reality
Contrary to popular belief, your spine isn’t the star player. Research shows hip muscles contribute 68% of the force compared to 22% from back tissues. Here’s the truth behind common misconceptions:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| “It’s a back exercise” | Hips/legs drive movement |
| “Grip limits progress” | Mixed grips extend capacity |
| “Heavy weights required” | Bodyweight variations build foundations |
“Your glutes and hamstrings are the engines – everything else just keeps the chassis intact.”
Understanding these roles helps optimize training. Focus on hip hinge mechanics rather than sheer back strength. Your body will thank you during yardwork and playtime with kids alike.
Proper Deadlift Technique for Safe Training
The foundation of safe strength training lies in precision mechanics. Mastering movement patterns ensures maximum benefit with minimal risk. Let’s break down the essential components of effective lifting form.

Building Your Foundation
Start with feet positioned under hips, toes pointing forward. The barbell should graze your shins – this alignment creates optimal leverage. Choose between these grip styles based on your needs:
| Grip Type | Best For | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Double Overhand | Light weights | Improves grip endurance |
| Mixed Grip | Heavy loads | Reduces bar roll |
| Hook Grip | Competition lifts | Requires thumb placement |
Engage shoulder blades by imagining squeezing a pencil between them. This creates crucial upper back tension before lifting. Keep chest lifted to maintain spinal alignment throughout the movement.
Executing With Precision
Follow these steps for controlled power transfer:
- Breathe deeply into your belly and brace core muscles
- Initiate movement by driving feet through the floor
- Keep barbell close to body during ascent
- Lock hips forward at full extension
“Your setup determines your success – rush it and you’ll fight the weight all day.”
Lower weights with the same care you lift them. Hinge hips backward first, then bend knees once the bar passes them. Maintain shoulder position over the bar during descent to protect your spine.
Exploring Deadlift Variations to Enhance Your Workout
Ever feel stuck in your strength training routine? Switching up your approach can reignite progress while targeting new challenges. Different lifting styles offer fresh ways to build power, address weaknesses, and keep sessions engaging.
Barbell Modifications for Specific Goals
The Romanian variation starts upright, focusing on controlled lowering to emphasize hamstrings and glutes. Perfect for developing explosive hip power, this style maintains constant tension through the entire posterior chain.
| Style | Setup | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Sumo | Feet outside hands | Reduces back strain |
| Trap Bar | Weight at sides | Easier on joints |
Sumo positioning shortens the lifting range, ideal for taller athletes. The trap bar’s neutral grip placement creates a more natural movement pattern, making it excellent for newcomers.
Balance-Building Alternatives
Single-leg versions transform this exercise into a stability challenge. Standing on one leg while lifting light weights:
- Reveals strength differences between sides
- Engages core muscles for balance control
- Improves coordination for sports performance
“Rotating variations every 4-6 weeks prevents plateaus better than any supplement.”
Beginners should master conventional form first. Intermediate lifters can add one variation weekly, while advanced athletes might cycle styles monthly for continuous adaptation.
Tips for Mastering Your Deadlift Form
What separates good lifters from great ones? The answer lies in preparation. Proper movement patterns begin long before you touch the barbell. Let’s explore how to build a bulletproof foundation.
Pre-Lift Preparation Essentials
Start every session with dynamic stretches. These activities prime your body for action:
| Warm-Up | Target Area | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Leg swings | Hip flexors | 1 min/side |
| Cat-cow stretches | Spinal mobility | 2 minutes |
| Bodyweight hinges | Hamstrings | 3 sets of 10 |
Beginners should practice the hip hinge motion using a broomstick. This teaches proper spine alignment without weight. Certified trainer Leah Simmons advises:
“Master the pattern first – the strength will follow naturally.”
Your body’s proportions affect your stance. Long-legged individuals might need wider foot placement. Tight shoulders? Try rolling a lacrosse ball across upper back muscles before lifting.
Watch for these red flags during practice:
- Knees collapsing inward
- Shoulders rounding forward
- Lower back arching
Fix these issues with wall drills. Stand back-to-wall and practice hinging until your glutes touch the surface. This reinforces proper knee and hip coordination. Remember – quality repetitions build safe strength faster than heavy weights ever could.

Integrating Deadlifts into Your Strength Routine
What if your workout plan could evolve as your skills improve? Smart programming turns this full-body movement into a growth accelerator. Let’s explore how to match effort levels with smart recovery strategies.
Customizing Rep Ranges
New lifters thrive with 3 sets of 5-8 reps, focusing on form mastery. Intermediate athletes might alternate heavy days (4×3) with volume sessions (5×10). Advanced trainees often use wave periodization – cycling intensities weekly to avoid burnout.
Recovery matters most. Allow 48-72 hours between sessions targeting similar muscle groups. Pair this exercise with upper-body days to balance workload. “Think of your nervous system as a battery,” says trainer Jenna Cole. “Don’t drain it completely.”
Strategic Exercise Pairing
Combine this lift with movements that complement its benefits. Try these effective combinations:
Power focus: Follow with box jumps or cleans
Hypertrophy focus: Pair with lunges or rows
Endurance focus: Alternate with planks or carries
Always prioritize progressive overload – add 2-5% weight weekly while maintaining clean technique. Remember, consistency beats intensity every time. Your future self will thank you when lifting suitcases or playing with kids feels effortless.

